RESTful Web Services
Representational State Transfer (RESTful) is an architectural style that defines how web services communicate within distributed systems. It follows standard constraints to ensure scalability, flexibility, and efficiency while abstracting component implementation and focusing on data exchange between elements.
RESTful APIs use lightweight formats such as JSON, XML, HTML, or plain text, making them fast, adaptable, and widely supported. Built on the HTTP protocol, REST remains the leading API standard powering modern web applications and integrations.
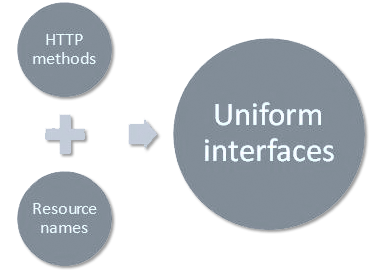
REST and HTTP: Understanding the Difference
Although REST and HTTP are closely related, they are not the same.
- REST is an architectural style that defines principles for building stateless, scalable web services through a uniform interface.
- HTTP is a communication protocol that enables interaction between clients and servers and is most commonly used to implement RESTful APIs.
While REST is protocol agnostic, HTTP provides the foundation for its methods – GET, POST, PUT, and DELETE – as well as for status codes. REST focuses on the representation of resources, whereas HTTP defines how that information is transmitted.
Artificial intelligence assists skilled developers by monitoring API behaviour, validating responses, and automating testing across REST and HTTP layers, improving reliability without replacing technical judgement.
Methodologies & Work Planning
For long term software development, structured methodologies ensure efficient project planning and execution. Agile development encourages adaptive planning, early delivery, and continuous improvement, offering flexibility to meet evolving business requirements.
A cross functional team, composed of professionals with diverse expertise, collaborates to achieve shared objectives. Beyond the technical dimension, effective project management (PM) relies on experience, transparent communication, and a sound understanding of business goals to align IT solutions with real world needs.