Understanding EU & Swiss Data Protection Standards
Since May 25, 2018, the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) has been the reference framework for data privacy across the EU, protecting individuals from the mass exploitation of personal data without consent.
Similarly, since 1 September 2023, Switzerland’s New Federal Act on Data Protection (nFADP / nLPD) aligns national law with the GDPR to:
✅ Strengthen personal data protection
✅ Adapt to technological evolution
✅ Maintain data exchange with the EU
✅ Support Swiss competitiveness
Who Is Concerned?
All organisations — whether in Switzerland or abroad — that process data of EU or Swiss residents, use cookies, tracking tools, or contact forms, are directly affected by GDPR/nLPD regulations.
Personal data includes any element that identifies a person directly or indirectly, such as:
📌 Name, email, phone number, IP address, biometric data, or browsing behaviour.
Main Compliance Principles
To comply, organisations must:
✔ Obtain explicit consent before collecting data
✔ Allow users to access, modify, or delete their data
✔ Secure personal data through encryption and limited access
✔ Maintain transparency in data collection and processing
The nLPD extends protection to biometric and genetic data, enforces privacy by design and by default, and focuses exclusively on natural persons.
Rights of Individuals
Under GDPR and nLPD, individuals benefit from:
✅ The right to be forgotten – deletion of personal data upon request
✅ The right to data portability – transfer between platforms
✅ The right to information – transparency on data use
✅ The right to object – refusal of profiling or marketing use
In case of a data breach, companies must promptly inform users and adopt preventive measures.
Obligations for Swiss Companies
Swiss entities handling EU residents’ personal data — even as subcontractors — must fully comply with GDPR.
They are required to:
🔹 Notify EU partners of any data breach
🔹 Obtain informed consent for profiling and marketing
🔹 Clearly identify themselves as data controllers or processors
🔹 Ensure transparency on how data is stored, used, and shared
Practical Implementation
To ensure compliance, businesses should:
1️⃣ Audit data flows – Know what data is collected and why.
2️⃣ Secure storage and transfer – Use encryption and SSL/TLS connections.
3️⃣ Train employees – Promote cybersecurity and data ethics.
4️⃣ Review third-party tools – CRMs, analytics, and cloud services must comply.
5️⃣ Publish a clear Privacy Policy – Detailing cookies, analytics, forms, and marketing use.
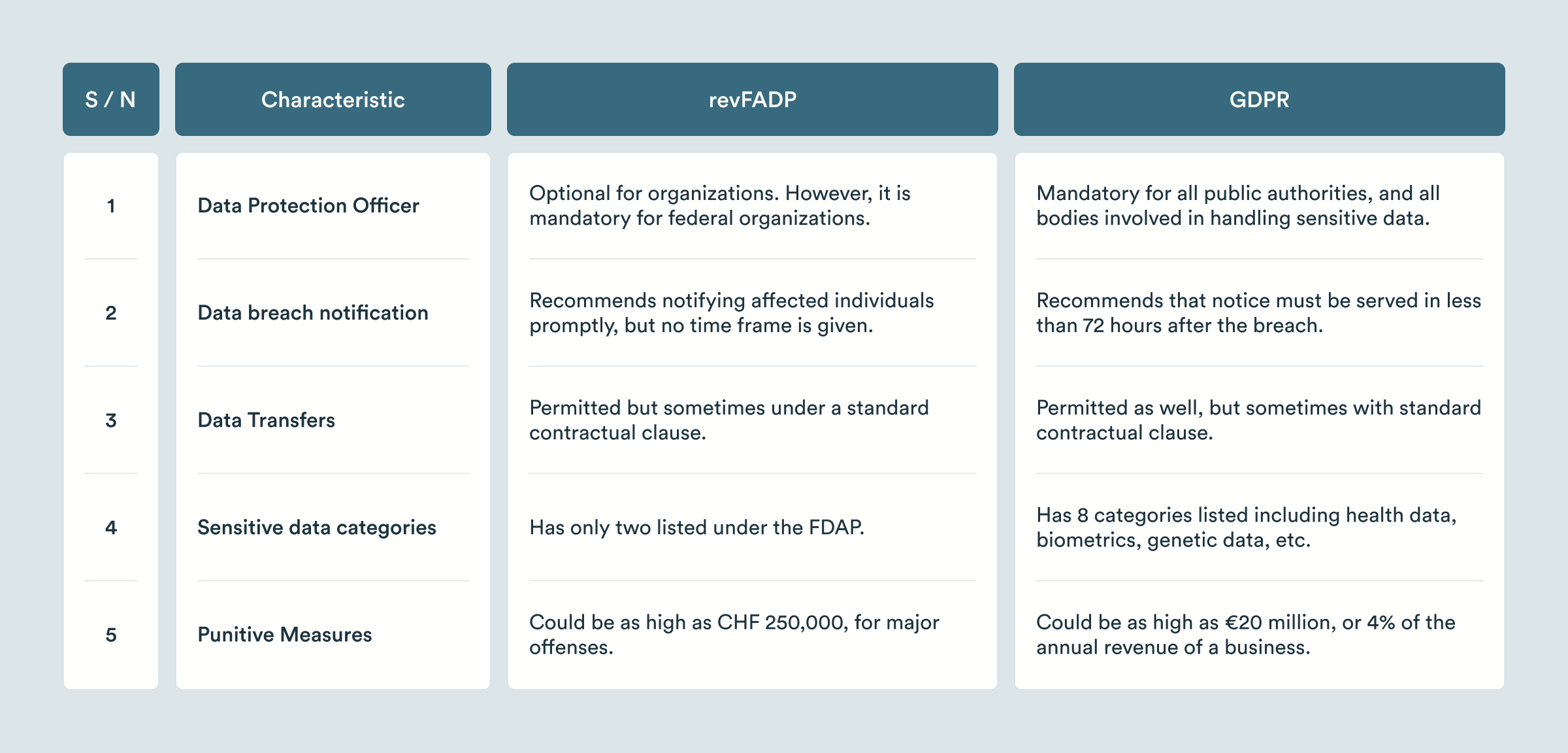
🇪🇺 Differences with the EU (GDPR vs. nFADP)
Recommended Resources
🔹 CNIL – GDPR Toolkit (EN)
🔹 Federal Data Protection and Information Commissioner (FDPIC)
🔹 ThinkData – Transparency Awareness Service
🔹 Preparing for the GDPR (PDF EN)
By integrating GDPR and nLPD best practices, companies not only ensure legal compliance but also strengthen user trust, digital ethics, and brand credibility.
DIGITALABS assists SMEs and professionals in implementing these standards — combining legal compliance, cybersecurity, and ethical data management.